
Scalp Seborrheic Dermatitis: Microbiome and Clinical Effect of a Novel Shampoo
September 23, 2025
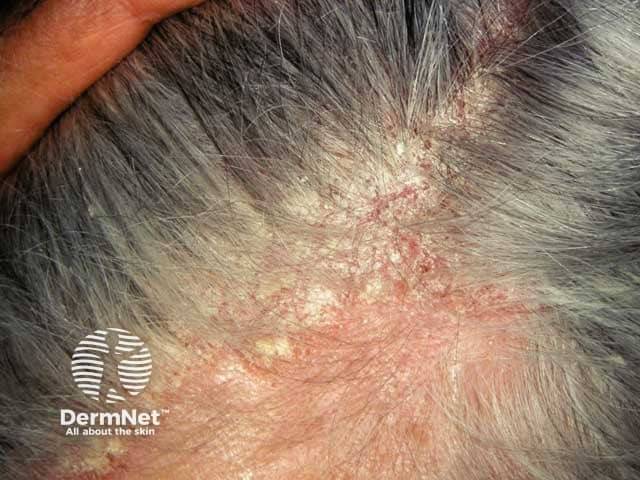
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) affects 1–5% of adults worldwide. While not contagious or related to diet, SD can be aggravated by illness, stress, tiredness, changes of season, and an overall deterioration of health status. This chronic inflammatory skin disorder can considerably impact quality of life and self-esteem, particularly due to the physical discomfort associated with persistent itching.
Scientific literature has linked scalp SD to an unbalanced microbiota, with increased populations of certain fungal and bacterial species. As a result, first-line therapies for mild-to-moderate scalp SD, which presents as dandruff but without visible inflammation, essentially rely on antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic topical agents.
To help expand the treatment options available for patients with this form of SD, a newly formulated anti-SD shampoo, containing two patented antifungal compounds (piroctone olamine and ciclopirox olamine) that work synergistically, a keratolytic compound (keluamid), and a soothing antioxidant agent (β-glycyrrhetinic acid), has been developed. In a randomized clinical trial involving patients with mild-to-moderate scalp SD, the shampoo demonstrated clinical efficacy for reducing the severity of dandruff, erythema, and scalp pruritus compared to a control group. Microbiota analyses revealed that the improvements in scalp symptoms were associated with the rediversification of the scalp microbiota. This included a significant increase in fungal and bacterial richness, a decrease in the level of SD-predominant Malassezia fungi and Staphylococcus bacteria, and an increase in the level of low-abundance fungi genera belonging to the Ascomycota phylum. Overall, these findings support the pivotal role of microbial rebalancing in alleviating SD symptoms.
Our medical writing team contributed to the publication of this study in Dermatology & Therapy: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40498389/
Reference of the publication: Maître M et al. Scalp Microbiome Dynamics Can Contribute to the Clinical Effect of a Novel Antiseborrheic Dermatitis Shampoo Containing Patented Antifungal Actives: A Randomized Controlled Study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025;15(8):2077-2097. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01408-z.
Image sourced from: DermNet